Introduction to Asthma
Asthma is a long time disease that impacts the airways in the lungs. It dilates or swells the airways thus making it hard to breathe. Asthma is associated with coughing, wheezing, breathlessness, and chest tightness. Unattended, this disorder, whose level varies, may interfere with a normal routine. It is important to understand asthma since it can be treated to avoid serious complications when realized early.

Definition of Asthma
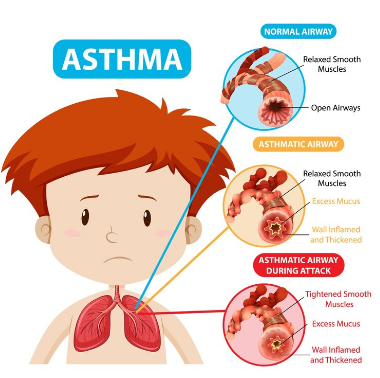
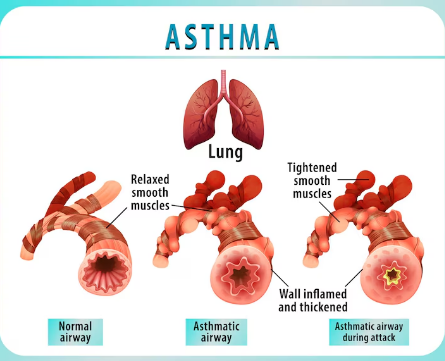
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory illness that constricts and dilates airways making the respiration process challenging. Due to the inflammation, the airways become vulnerable to various triggers, such as exercise, smoke, dust and pollen. The presence of these triggers makes breathing more challenging as the muscles around the airways tighten and the amount of mucus secreted increases. We refer to this as an asthma attack. Even though asthma does not have a cure, with the appropriate care it can be managed.
Understanding the Respiratory System
Learning about the way respiratory system works is useful in the understanding of asthma better. When you breathe, air flows into your lungs via bronchi that are airways running through your mouth or nose. These bronchi become constrained and inflamed when these patients experience an asthma attack. This limits the circulation of air, leading to wheezing or shortness of breath. Normal lung expansion and contraction is not hindered in asthma as a result of swelling and collection of mucus.
Types of Asthma
There are many types of asthma and their symptoms and causes are different. The type is useful in determining the most optimal course of action. Among the primary kinds are:
1. Asthma with allergies
induced by allergens like dust mites, pollen or pet dander. It is the commonest type of asthma and is often related to allergic reactions or family history.
2. Asthma Without Allergies
This type is caused by such factors as cold air, stress or infections as opposed to allergies. Any age can be impacted.
3. Asthma at Work
resulted due to occupational exposure to gases, dust or chemical fumes. It is gradually developed by people working in factories, farms, or labs.
4. Asthma Caused by Exercise
occurs after or before the exercise. Some of the symptoms include coughing, tightness in the chest, or wheezing at the time of exercise.
5. Asthma in childhood and Adulthood.
Age may be any age at all as the onset of asthma. Adult-onset asthma often requires long-term management unlike childhood asthma which could improve with age.
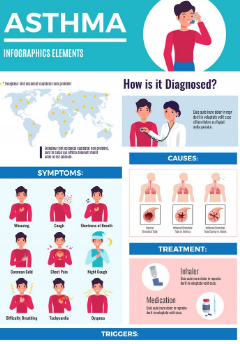
Causes of Asthma
Environmental and genetic factors combine together in causing asthma. The combination of many triggers but not one causes the symptoms.
Genetic Factors: The risk level is elevated in the case of a family history of allergies or asthma. When a child has one parent with asthma, he or she will have a high chance of developing it.
Environmental triggers: The lungs can be irritated by dust, smoke, pollen, and air pollution and lead to asthma.
Respiratory Infections: Childhood infections by viruses can cause permanent damage to airways.
Occupational Exposure: The chemicals, industrial fumes, and strong odors have the ability to trigger asthma symptoms.
Lifestyle and Diet: Lifestyle and dietary habits including poor diets, obesity, and inactivity may aggravate asthma symptoms.
It is crucial to discover the personal triggers of asthma of each individual to be able to take control of the disease.

Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms may be mild or even lethal. They may appear once in a while or every day depending on the severity of the condition. The common signs and symptoms are:
Shortness of Breath: Breathing difficulty ensues especially at night time or during exercises.
Wheezing: This is a whistling noise that occurs when airways are constricted during breathing out.
Coughing: A cough that persists and becomes worse in the morning or during the night.
Chest Tightness: The feeling of being heavy or forced in the chest.
Sleep disturbance: The client is unable to fall asleep due to dyspnea or coughing.
These symptoms are often aggravated by stress, cold air and exposure to allergens. Routine monitoring helps in effective control of them.
Asthma Triggers
The triggers refer to things or situations that increase the symptoms of asthma. These triggers are important to the prevention of attacks.
- Typical Causes of Asthma
- Pollen and dust mites
- Dander from pets
- Air pollution and cigarette smoke.
- A sharp drop or fall in temperature or a cold weather.
- Powerful smells, perfumes or sprays.
- Exercise without warming up.
Anxiety or emotional tensionAccording to the issues of asthma attacks, their frequency and severity can be reduced significantly through the awareness and avoidance of the triggers.
Diagnosis of Asthma
Proper diagnosis is vital before commencement of treatment. Physicians confirm asthma through various tests and review of medical history.
Procedure for Diagnosis:
Medical History: The doctor gets the symptoms, triggers and family history.
Physical Examination: examination of lungs using stethoscope to determine the presence of wheezing.
The spirometry test also identifies the rate at which you get to exhale air and the volume.
Allergies tests: Find out what allergens could be causing symptoms.
Peak Flow Measurement: A simple test to monitor the performance of lungs at home.
Early diagnosis makes it possible to achieve a better management and to reduce the long-term lung damage.
Treatment and Management of Asthma
Asthma is a disease that cannot be cured but can be treated successfully with the help of medication, a change in lifestyle, and avoiding triggers.
1. Medication inhalers:
This is the most used and effective medication treatment.
Preventive inhalers (also known as long-term control)
Oral drugs: anti-inflammatory pills or syrups.
Nebulizers are gadgets, which spray medication directly into the lungs.
2. Management of Lifestyle
It is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle in managing asthma.
Avoid pollution and smoking.
Eat nutritious foods that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins.
Breathing and meditation can be used to relieve stress.
3. Regular Health check-ups.
Periodical visits to a medical practitioner can help in medication correction and in monitoring progress. It is also recommended to maintain an asthma journal so as to track symptoms.
Prevention of Asthma Attacks
Prevention is aimed at making the lungs stronger and reducing triggers.
Avoid and Recognize Triggers: avoid allergens and irritants that exacerbate asthma.
Keep a Clean House: Clean the house using air cleaners and wash your beddings regularly to eliminate dust mites.
Keep up with Vaccinations: Immunization against pneumonia and the flu can prevent diseases that may worsen asthma.
Keep Your Weight in Check: Asthma symptoms may be made worse by being overweight.
Direct administration of medicines is best: Do not forget to take your medications and do not exceed the prescriptions given by your physician.
With these precautions, there is fewer and less severe asthma attacks.
Asthma in Children
Rain tapped against the window, soft and steady. It fit the hush inside, almost like the house had its own heartbeat. Out there, everything faded into gray, but in here, the fireplace glowed and wrapped the room in warmth. I pulled my knees up in the chair and opened a book. The story took over—page after page, I sank right in. Time didn’t matter. The rain made the world feel small and safe, like nothing could reach me. Just words, warmth, and a quiet that asked for nothing more.
Asthma in Adults
Obesity, breathing in irritants, and getting respiratory infections all play a part in adult-onset asthma. Managing it isn’t just about taking medicine now and then—you’ve got to keep an eye on things and stick with your treatment for the long haul. It really helps when adults steer clear of triggers and actually follow their plan. Simple changes, like quitting smoking or keeping your space clean, make a huge difference.
Complications of Asthma
If you don’t treat asthma the right way, things can get pretty rough. People end up in the hospital more often because of bad attacks. The airways can actually change shape for good, making it harder to breathe. You feel tired, you can’t sleep well, and just moving around gets tougher. It’s not just your body, either—anxiety and stress sneak in too. But act fast and treat asthma properly, and you dodge all that. Life just gets a lot better.
Problem-Solving Tips for Asthma Management
Here’s how you can take control of asthma without feeling overwhelmed:
Start by working with your doctor to build a real action plan—one you know how to use when things get rough or symptoms start flaring up. Check your breathing every day with a peak flow meter so you actually know when something’s off, not just when it feels that way.
Keep your inhaler close, always. You never know when you’ll need it, and scrambling to find it during an attack is the last thing you want. Make sure your family knows what to do if you have an asthma attack. It takes the pressure off you and keeps everyone safer.
And hey, don’t ignore tech. Smart inhalers and tracking apps make it way easier to keep up with your symptoms and meds. All of this puts you in the driver’s seat with your health, not just along for the ride.
Latest Research and Advances
Asthma’s always been a bit of a mystery, but researchers are getting closer to cracking it. For people who really struggle with asthma, biologic therapies are changing the game. These treatments go after specific parts of the immune system—and honestly, they’ve changed the game for a lot of people. Now, doctors have smart inhalers and AI monitors at their fingertips, so they can actually keep an eye on how someone’s doing day by day. At the same time, scientists are diving into genetics and the environment, trying to understand why some people getasthma and others don’t. With all these breakthroughs and more personalized options coming soon, managing asthma feels way more hopeful than it did just a few years ago.
Conclusion
Asthma’s pretty common—millions of people deal with it every day. Sure, it sticks around for the long haul, but with the right treatment, most folks keep it in check. If you get what asthma actually is, what usually triggers it, and how symptoms show up, you’re already a step ahead. Honestly, most people with asthma do just fine. They take their meds, try to stay healthy, and watch out for the stuff that sets them off. Regular check-ups and learning more about asthma really help too. In the end, staying consistent makes all the difference.
