LVF (Left Ventricular Failure) – Understanding the Condition and Protecting Your Heart
Heart health is key to living a long and active life, and not all people understand the presence of such dangerous conditions as left ventricular failure (LVF). LVF is one type of heart failure that interferes with the ability of the heart to pump blood effectively. The awareness of this condition, early symptoms identification, and preventive action can help you save your heart and improve the quality of your life.
What Is LVF (Left Ventricular Failure)?
The inability of the left ventricle of the heart to pump blood efficiently to the rest of the body leads to LVF also known as left ventricular failure. The left ventricle supplies all the organs and tissues with oxygen-rich blood. The blood in its weakened state may cause breathlessness and build up of fluid in the body by backing up into lungs.
LVF is a severe condition, and therefore, it should be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible. It can come as a result of many heart diseases, including hypertension, valve issues, or coronary heart disease.
Causes of LVF
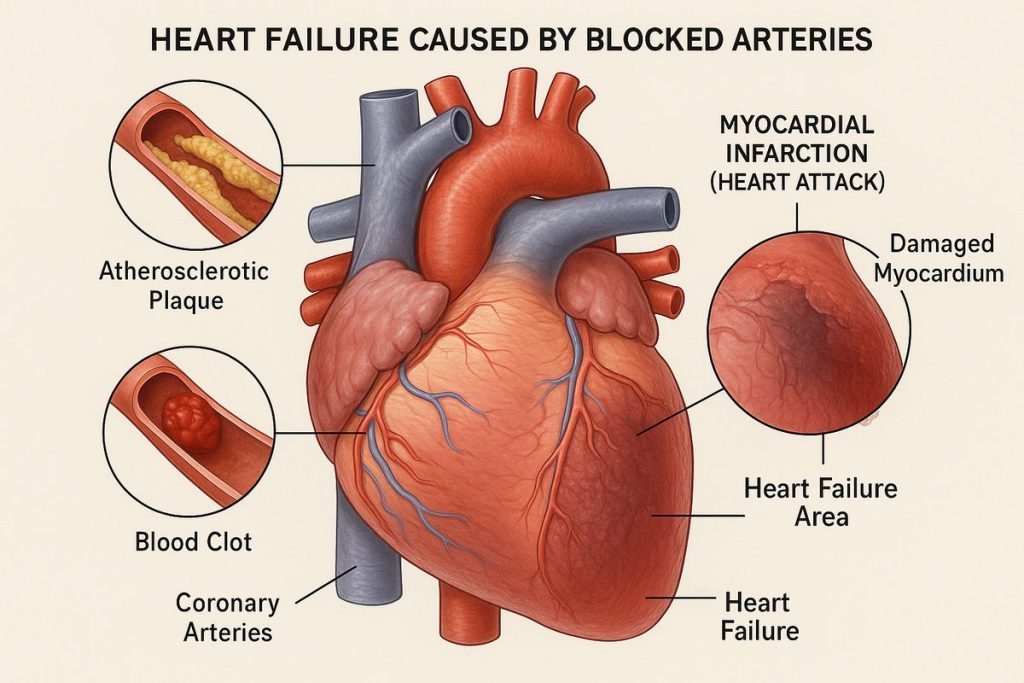
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD):
The heart muscles become weaker with the passing of time as the blood flow to the arteries is reduced.Hypertension or high blood pressure causes the heart to overstrain with time which ultimately strains the left ventricle.
Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction):
A heart attack is the condition that causes the heart to lose its ability to pump blood effectively by destroying the tissue.
Valve Diseases:
The left ventricle experiences extra strain when the valves of the heart are the ones that are narrow or leaking.
Cardiomyopathy:
A disease where the heart muscles either enlarge, thicken or harden.
The prolonged abuse of drugs or alcohol may cause the heart to become weaker and this may lead to heart failure.
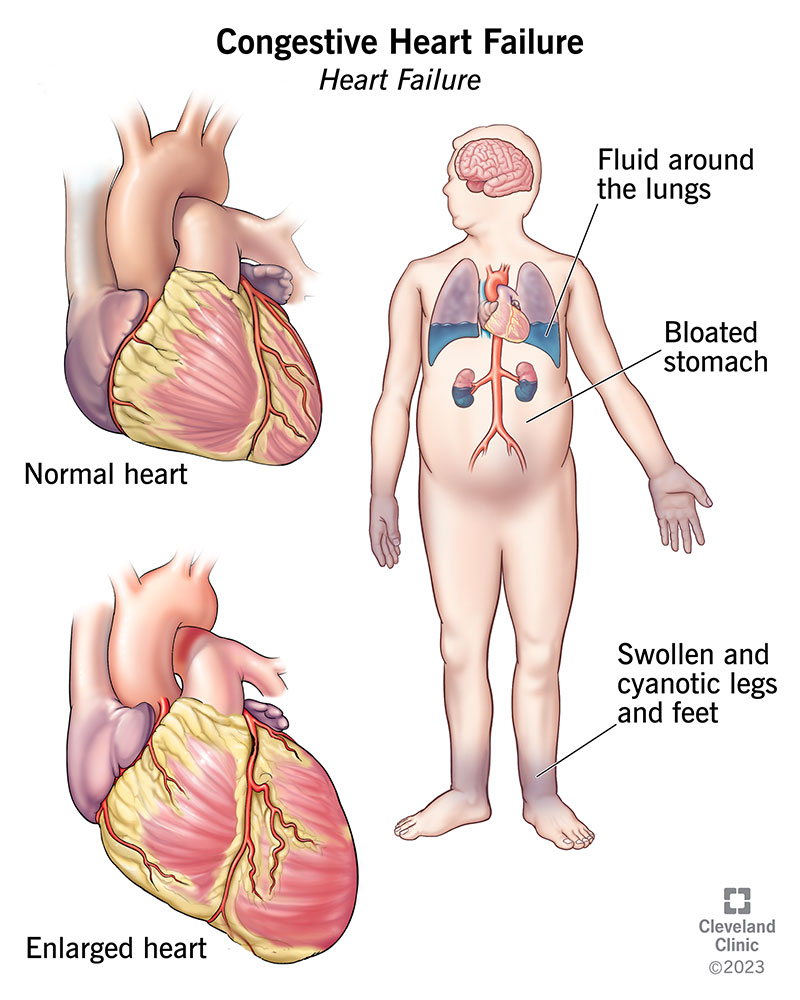
Common Symptoms of LVF
The important part of LVF treatment is to recognize the symptoms at an early stage. The symptoms can either come gradually or abruptly, depending on the rate at which the heart performance deteriorates.
Key Symptoms Include:
Shortness of breath especially when lying or exercising.
Drowsiness and fatigue due to deficiency of blood flow.
Wheezing/chronic cough with or without pink frothy sputum.
Pitting ankle, foot or leg (because of fluid retention).
Difficulty breathing and hence sleeping problems.
Sudden gain of weight because of fluid retention.
Seek medical attention in case you or any other person you are acquainted with have them.
How LVF Affects the Body
With the development of LVF, the left side of the heart is not able to supply adequate oxygenated blood to the body requirements. This makes blood accumulate behind the lungs thereby congesting and making it difficult to breathe. The resulting low oxygen levels impact on all organs such as the brain, kidneys, and the muscles causing the patients to be tired and weak.
Untreated LVF may eventually develop into a more advanced type of the disease, known as congestive heart failure (CHF) in which both sides of the heart fail. This renders prompt diagnosis and follow up very significant.

Diagnosis of LVF
There are several tests conducted to ascertain left ventricular failure (LVF). These consist of:
Physical assessment:
Evaluation of respiratory rates, cardiac arrhythmia, and peritoneal edema.
An echocardiogram (ECHO) is a heart ultrasound, which is an indicator of the pumping efficiency of the left ventricle.
Blood tests:
Help to assess particular cardiac markers, and kidney work.
An MRI or CT scan of the heart gives detailed images of the anatomy and injury of the heart.
Treatment Options for LVF
Treatment of LVF is dependent on the severity of the condition and the cause of the condition. The goals include improvement in heart functioning, decreasing the symptoms and preventing complications.
Medications
Doctors often prescribe such drugs as:
Beta-Blockers: slow down the heart rate and enhance the effectiveness of the pumping of the heart.
Diuretics: This helps the body to rid itself of excess fluid and this reduces the swelling and dyspnea.
Aldosterone Antagonists: Reduce the accumulation of fluid and sodium.
Vasodilators: Dilate the blood vessels to increase the pumping of the heart.
Medical Devices
There are patients who might require devices to avoid sudden cardiac arrest such as implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) and devices to regulate abnormal heartbeats such as pacemakers.
Surgery
In severe cases, the patient may need transplantation of the heart, repairing of valve, or bypassing.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing LVF
Lifestyle is crucial in order to control a left ventricular failure and prevent its further development. Even minor changes can affect the health of the heart greatly.
Healthy Lifestyle Tips:
Eat a lot of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meat, and low-fat dairy products to ensure the heart is healthy. Avoid fried and salty food.
Get Exercising: Cardiovascular exercises which allows the heart to work more efficiently and pump more blood through the blood vessel vessels would include yoga, bike riding, and walking.
Keep Track of Your Daily Weights: This is also an indicator of fluid retention and could occur suddenly.
Stress management: Measures that include sleeping, relaxation, and meditation are among those that relax the heart.

Preventing LVF – Steps to Protect Your Heart
It is always better to prevent than cure. This may be achieved by keeping your heart healthy, thus reducing the risk of LVF, among other diseases of the heart.
Manage Blood Pressure:
One of the major causes of LVF is high blood pressure. The number of times you are checking your blood pressure and taking your medicine since you are prescribed to do so.
Control Diabetes and Cholesterol:
Cholesterol and high blood sugar destroy the tissues of the heart and blood vessels. Control by means of drugs and diet to keep them at normal level.
Keep Your Weight in Check:
Being overweight leads to greater pressure of the heart. Slow weight loss is the desired but a balanced lifestyle must be taken up.
Stay Active:
Exercising every day in moderate workouts of up to 30 minutes makes the heart strong and the blood circulation better.
Avoid Excess Salt:
The fact that salt exacerbates the LVF symptoms is due to its retention. Avoid junk food and minimize the use of salt in food.
Living with LVF – Coping and Emotional Health
Even though the diagnosis of LVF may be devastating, its patients can still live active and fulfilling lives by providing appropriate care. Engaging the family into care, talking to medical professionals, and being part of support groups can all be quite substantial.
Physical and emotional health are also very crucial. Anxiety and depression are common in LVF patients, and having a positive attitude, practicing mindfulness and seeking counseling can be highly helpful.
When to See a Doctor
You should call your doctor right away in case you have one of the following symptoms:
Chest pain or sudden dyspnea.
Bloated stomach or legs.
Unconsciousness, lightheaded, or palpitations.
Continuous mucus coughing.
Heart functioning can be improved and hospitalization can be avoided with early treatment.

Conclusion – Take Charge of Your Heart Health
Left Ventricular Failure or LVF is a very dangerous, though treatable disease. By early diagnosis, medication, lifestyle change and regular checkups, patients will be able to live active and healthy lives. The knowledge is the first step to safeguard your heart; you can be in control of your heart by recognizing the symptoms, preventing risk factors and doing what your physician has asked you to.
Take care of your heart today in order to secure a better tomorrow.